IPS Design conventions and principles 1
Contents
- 1 Design conventions and principles
- 1.1 How to use terminologies (preferred binding)
- 1.2 Representing "known absent" and "not known"
- 1.3 Uncoded information
- 1.4 Unmapped Coded Concepts
- 1.5 Mapped coded concepts
- 1.6 Translation of designations
- 1.7 Narrative Translations
- 1.8 Medicinal Product Identifications
- 1.9 Medication Statement
- 1.10 Provenance
- 1.11 General Implementation Guidance
Design conventions and principles
How to use terminologies (preferred binding)
As stated above, to be universally exchangeable the International Patient Summary must rely on international multilingual reference terminologies. To that effect, each codeable element of the international patient summary template is bound to a Value Set built upon an international reference terminology, such as SNOMED CT, LOINC, UCUM, EDQM Standard Terms. These reference terminologies have been selected to provide the preferred bindings for the codeable elements of the patient summary. They are the primary terminologies of this specification.
Nethertheless, it is anticipated that in some situations, a system producing an instance of patient summary might not support one or the other of these primary terminologies, supporting only a local inteface terminology instead. Similarly, it is also anticipated that the receiving system might in some cases not be able to use a code in a patient summary, either because this code belongs to a primary terminology that the receiving system does not support or because this code belongs to an interface terminology specific to the country of the producing system.
In order to maximize the international scope and usability of patient summaries, and also to accommodate the exceptional situations listed above, this specification makes these requirements:
- The Primary Code of a codeable element should be populated.
- If populated, the Primary Code of a codeable element shall be chosen from the primary terminology assigned to the value set bound to this element.
- The Display Name of the Primary Code shall be populated with a term representing this same code in the primary terminology, in the language chosen for the current instance of the patient summary.
- When the Primary Code is not populated, the Original Text shall be populated with a textual expression representing the meaning for the producer.
- One or more Alternate Codes from a local interface terminology may be provided, each with its associated Display Name.
Primary Code
In the data type for codeable elements (CD constrained by the CD.EPSOS template), the Primary Code is represented by the attributes @code, @displayName, @codeSystem, @codeSystemName, @codeSystemVersion.
Alternate Code
In the data type for codeable elements (CD constrained by the CD.EPSOS template), an Alternate Code is carried in a "translation" sub-element.
Original Text
In the data type for codeable elements (CD constrained by the CD.EPSOS template), the Original Text is provided in the "originalText" sub-element.
Representing "known absent" and "not known"
In line with the properties of minimalism and non-exhaustiveness for the IPS (see the IPS definition above), and benefiting from the experience acquired with the European cross-borders services, this guide explicitly addresses two general situations:
- condition or activity unknown;
- condition or activity known absent.
Other kinds of negations such as: (a) the negation of an allergy to a specific agent; (b) the absence of a particular disease; or (c) the fact that a specific vaccination has not been performed; have been considered beyond the set of essential data for an IPS, even if it is not precluded to provide them.
This specification represents this core set of negations (“condition/activity unknown” and “condition/activity known absent” ) by leveraging the expressiveness of SNOMED CT to use explicit coded elements rather than relying on specific mechanisms of the underlying syntactical standard (such as nullFlavor and negationInd attributes for CDA).
The main reasons for this choice are:
- @negationInd in CDA has been superseded in V3 later by two other negation indicators: @actNegationInd and @valueNegationInd.
- To have a representation of the clinical content of the patient summary which is less dependent on a particular format or syntax, enabling a more practical path to transforming and exchanging data from one standard format (e.g., CDA R2) to another (e.g., FHIR).
- to provide one single method to express either the presence or absence of a particular condition (e.g., an allergy) or activity (e.g., an immunization), or the lack of knowledge regarding this kind of condition or activity, resulting in a more robust and easily implementable specification.
In some cases this required the creation of new SNOMED CT concepts. For example, a known absent Allergy/Intolerance would be represented by "716186003 |No known allergy (situation)|" (or any combination of its descendants), whereas no information about Allergy/Intolerance would be represented by a code with the meaning "Allergic disposition not known (situation)". For these cases an HL7 extension to SNOMED CT has been created, working for their future inclusion in the SNOMED CT International Release.
For the other kinds of negations, not explicitly mentioned in this guide, it is suggested to apply – where possible – the same approach. Future versions of this guide may extend the number of cases covered and include new coded concepts for supporting them.
Uncoded information
An IPS originator may not be able to value a coded element with an appropriate coded concepts, but only with textual information. This may happen for two reasons:
- the originator is not able to express the concept in the reference value sets;
- the originator is not able to express the concept in any known terminology.
The first case, assuming that the coding strength is CNE (coded, no extensions), is represented in this guide with the following assertion:
xxxxxxx
<code codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.96" nullFlavor="OTH">
<originalText>
<reference value="#ref1"/>
</originalText>
</code>
xxxxxxxx
That is expressing that there are no codes applicable in the referred code system (in the example SNOMED CT). Please note that according to this guide the text is documented in the section narrative and only referenced by the coded element.
Note: datatype R1 doesn't allow to specify that there are no codes applicable in the referred value set, as instead possible with datatype R2. Future versions of this guide may consider to extend the datatype to better support this situation.
The second case, that applies both to CNE and CWE (coded with extensions) coding strengths, is instead here represented valuing the coded element with the most generic nullFlavor “NI” (No Information) and pointing the text in the section narrative:
<value xsi:type="CD" nullFlavor="NI">
<originalText>
<reference value="#ref1"/>
</originalText>
</value>
Note: the most proper nullFlavor to be used here would be "UNC" (Uncoded) but this code is not part of the nullFlavors foreseen by the CDA R2 standard.
Unmapped Coded Concepts
In several real world situations the records used as source for the Patient Summaries may use locally adopted terminologies mapped into the reference value sets. When the original coded concept cannot be mapped in one of the coded concepts included in the reference value sets, is recommended that the original code is reported in the IPS instance as well as the indication that the mapping didn’t occur. (See also the Concept code mapping in the functional requirements section.)
Two circumstances are here considered: the case in which the coding strength is CNE and when it is CWE.
In the case of coding strength CNE the following statement can be used to express that no appropriate target coded concepts were found:
<value xsi:type="CD" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.96" nullFlavor=”OTH”> [ <originalText><reference value='#ref1'/></originalText>] <translation code="A02.9" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.3" displayName="Infezioni da Salmonella non specificate"/> </value>
The square brackets [ ] are used to indicate that the originalText element may or may not be present
Note: It may happen that a mapping would be possible in the target code system, but not in the target value set; datatype R1 doesn't allow to specify this difference, that is that there are no codes applicable in the reference value set, as instead possible with datatype R2. Future versions of this guide may consider to extend the datatype to better support this situation.
Even if, in case of CWE coding strength, it would be allowed to leave the orginal code as the primary code, this guide suggests that to highlight that a mapping to the reference value set was attempted and no suitable target codes were identified, it is reccomended to represent the original code in the <translation> sub-element and value with a nullFlavor the main coded element.
<value xsi:type="CD" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.96" nullFlavor=”NI”> [ <originalText><reference value='#ref1'/></originalText>] <translation code="A02.9" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.3" displayName="Infezioni da Salmonella non specificate"/> </value>
The square brackets [ ] are used to indicate that the originalText element may or may not be present
Mapped coded concepts
As mentioned above in several circumstances an original coded concept is mapped into the reference value sets. When this happens both the original and the reference codes should be reported in the IPS instance. Other conditions that should be considered are described in the Concept code mapping in the functional requirements section, and refer to the multiple coding; the preservation of the link to the original text; the mapping between a same code system.
All those aspects are considered in this section.
The simplest situation is the case of a single code mapped into a reference one, with original and reference codes belonging to different code systems. Hereafter the way to represent it:
<value xsi:type=”CD” code="42338000" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.96" displayName="Salmonella gastroenteritis">
[ <originalText><reference value='#ref1'/></originalText>]
<translation code="003.0" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.103" displayName="Gastroenterite da Salmonella"/>
</value>
The square brackets [ ] are used to indicate that the originalText element may or may not be present
The second example is the case in which the originator provides a multiple mapping. In this case if the primary code is one belonging to the reference value set noting should be done.
If not, as in the example below, all the original primary and alternate coded concepts are represented in a nested translation element, as described by the following example:
<value code="422479008" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.96" codeSystemName="SNOMED CT" displayName="FEMALE BREAST INFILTRATING DUCTAL CARCINOMA, STAGE 2" xsi:type="CD">
<originalText><reference value="#problem4name"/></originalText>
<translation code="code-example" codeSystem="1.999.999" codeSystemName="this is only an example" displayName="FEMALE BREAST INFILTRATING DUCTAL CARCINOMA, STAGE 2">
<translation code="174.9" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.103" codeSystemName="ICD-9CM" displayName="Malignant neoplasm of breast (female), unspecified"/>
<translation code="C50.919" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.90" codeSystemName="ICD-10-CM"displayName="Malignant neoplasm of unspecified site of unspecified female breast"/>
</translation>
</value>
The third case is when the original and the reference coded concepts belong to the same code system (distinct codes). This may be the result of a different level of granularity between the original and the reference value sets.
<code code="60591-5" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.1" codeSystemName="LOINC" displayName="Patient Summary"> <translation code="60592-3 " codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.1" displayName="Patient summary unexpected contact "/> </code>
Note: the R1 datatype definition identifies the <translation> as “a set of other concept descriptors that translate this concept descriptor into other code systems.”; there is however a common understanding that it “may be more than on representation in a single code system where code systems allow multiple representations, such as Snomed-CT”. Datatype R2 extended in fact the possibility to provide translations also in the same code system.
Translation of designations
The capability of recording one or more designations, in different languages, for the exchanged Patent Summary is one of the functional requirements requested for “safety and liability reasons” by the European Cross-border services (see Designations’ Translation under the Functional requirements and high-level use cases for more details).
It is known that there is not a “native” way to convey this kind of information using the coded descriptor (and derived) datatypes, in fact the @displayName attribute has cardinality 0..1 and the <translation> was designed for the coding translation, “that is to translate this concept descriptor into other code systems” and not for the translation of designations.
Note for balloters:
two options has been discussed and reported in this ballot version of this guide to collect feedback from ballotters.
- The first one is base on an optional extension to the CD datatype ;
- The second one doesn't require extensions, but some flexibility in the use of the <translation> element.
these two options are not mutually exclusive.
The first solution is based on an optional extension to the CD datatype ; A description of the extended CD and CE datatypes is provided in the Datatypes section.
Hereafter some examples of possible use of this extension in case of
No code mapping
<code code="60591-5" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.1"codeSystemName="LOINC" displayName="Patient Summary">
<ips:designation lang=”it-IT” value="Profilo Sanitario Sintetico" />
<ips:designation lang=”fr-FR” value="Patient Summary" />
<ips:designation lang=”en” value="Patient Summary" />
</code>
Codes mapping
<value xsi:type=”CD” code="42338000" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.96" displayName="Salmonella-gastroenterit">
<ips:designation lang=”da-DK” value=" Salmonella-gastroenterit" />
<ips:designation lang=”en” value="Salmonella gastroenteritis (disorder)" type=”FSN” />
[ <originalText><reference value='#ref1'/></originalText>]
<translation code="003.0" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.103" displayName="Gastroenterite da Salmonella"/>
</value>
The second one doesn't require extensions, but it some flexibility in the use of the <translation> element.
In this case the language code can be declared.
No code mapping
<code code="60591-5" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.1"codeSystemName="LOINC" displayName="Patient Summary">
<translation code="60591-5" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.1"codeSystemName="LOINC" displayName="Profilo Sanitario Sintetico" />
</code>
Codes mapping
<value xsi:type=”CD” code="42338000" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.96" displayName="Salmonella-gastroenterit">
[ <originalText><reference value='#ref1'/></originalText>]
<translation code="42338000" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.96" displayName="Salmonella gastroenteritis">
<translation code="003.0" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.103" displayName="Gastroenterite da Salmonella"/>
<translation />
</value>
Narrative Translations
With “narrative translation” is meant both the translation of the original narrative text, that can be human curated or automatically performed; and the generation of a translated narrative based on the coded entries.
The functional requirements associated to this process are described in the Designations’ Translation under the Functional requirements and high-level use cases section, and can be summarized in two main points : (a) language identification and (b) distinguishable original and translated narratives. It would be moreover good if the methodology applied for the narrative translation (e.g. derived from the coded entries; translated by a generic service;..) should be recognizable.
Considering that only one <text> element is allowed for section, the solution suggested by this guide is to document the narrative translations into subordinate sections (one for translation) as described by the template 2.16.840.1.113883.10.22.3.15.
Hereafter an example:
<section>
<templateId root="2.16.840.1.113883.3.1937.777.13.10.5"/>
<id root="1.2.3.999" extension="--example only--"/>
<code code="48765-2" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.6.1" displayName="Allergies and adverse reactions"/>
<title>Allergies and Intolerances</title>
<text>No known Allergies</text>
<!-- OMISSIS -->
<component>
<section>
<!-- subordinate section carrying a translation of the parent section -->
<title>Allergie ed Intolleranze</title>
<text>Nessuna Allergia Nota</text>
<languageCode code="it-IT"/>
</section>
</component>
</section>
Medicinal Product Identifications
The identification of medicinal products – that in general is quite-easily solved within a single jurisdiction relaying on local drugs databases – is instead one of the major still open issue for cross-jurisdictional services.
The set of ISO standards call IDMP [ref] - designed initially for the regulatory scopes, but hopefully extensible to other domains- are the most promising solution for solving this known issue as also highlighted by the European project OpenMedicine [ref]. The completion of the IDMP implementation guides; the deployment of the needed supporting services; the development of some companion standards that will allow the seamless flow of the IDMP identifiers and attributes from the regulatory space to the clinical world (and back) are however still in progress. Some further years are needed before these identifiers and attributes will be available for actual use.
Following therefore the IPS principles of “implementability” and “openness and extensibility” the solution here proposed will not then rely on the IDMP identifiers; being however already suitable for representing the IPS relevant IDMP identifiers and attributes: e.g. Pharmaceutical Product Identifiers (PhPIDs); Medicinal Product Identifier (MPID); Medicinal Product Package Identifier (PCID).
Note for ballotters: IPS members had no access to the latest version of the IDMP implementation guides; any indication that may help the alignment with those standards would be appreciated.
Note: IDMP Medicinal Product (MPID) and Medicinal Product Package (PCID) identifiers depends on the market authorization, the “same” product might therefore have different IDs if different authorizations have been required in different countries (the PhPID should be however the same). For the purpose of the IPS it might be useful if in future standards will be defined new global product identifiers that are independent by the drug registration process (as the Virtual Medicinal Product in SNOMED CT) and related to the IDMP identifiers.
Thus, in absence of a global identification system for products, the solution here proposed is based on the approach initially adopted by the European cross-border services (epSOS and currently by the eHDSI project), then reused by the IHE Pharmacy templates and more recently adopted (for specific cases) also by the HL7 Pharmacy Medication statement templates. The main idea is in fact that of integrating possible local drug identifiers (e.g. product codes) with all the relevant identifying and descriptive attributes that may help the receiver to understand the type of product the sender is referring to, e.g.: active ingredients; (administrable) dose forms; strengths; route of administration; package description.
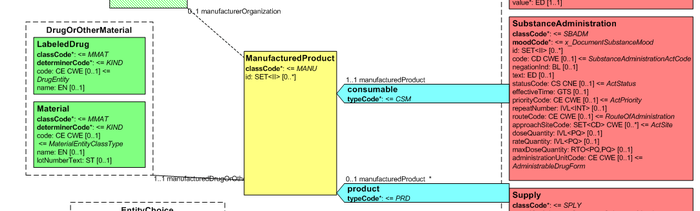
Medicines data are usually represented in the CDA Templates using the class manufacturedMaterial, that includes a code and a name used for describing any level of product: packaged product, medicinal product, classes or clusters or products, and so on. This information is not however sufficient for covering the defined needs.
[Figure 1] Representation of medicines in CDA
Hence, in order to be able to describe these attributes an extension of the CDA model needs to be applied and this was done in epSOS enhancing the Manufactured Product and Material classes from the CDA model with the attributes and relationships derived from the Medication and Medicine classes from the R_Medication CMET.
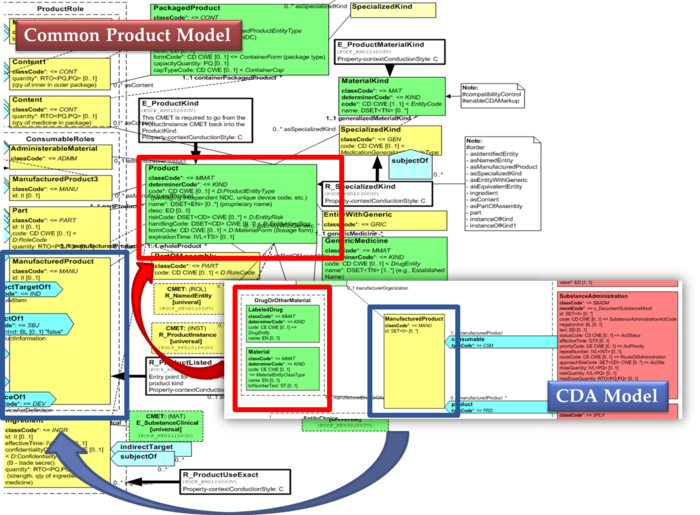
The same design approach has been followed for this guide adopting the Common Product Model (R_ProductListed) instead.
This choice has been made:
- considering the expected use of this model (“The common product model is used to improve the alignment between the different representations of products used within the body of HL7 Version 3 models. One goal of this effort is to make it possible for there to be a single such representation, which could then be used as a common message element type (CMET) across those models.”)
- to eventually have a common implementable solution to represent the future IDMP identifiers and attributes in the IPS and in other document based standards (as SPL).
[Figure 2] shows how the CDA model has been enhanced with the Common Product Model: the relationship and classes of the CPM manufactured material (Product) class has been added as extensions to that of the CDA model (Material); the same has been done for the ManufacturedProduct classes.
[Figure 2] CDA model and the Common Product Model
Medication Statement
Provenance
In the development of this Implementation Guide, consideration was given to the HL7 CDA® Release 2 Implementation Guide: Data Provenance, Release 1 - US Realm Draft Standard for Trial Use (December 2015). That guide provides a matrix offering a thorough and systematic analysis of provenance characteristics of electronic health records. Given the agreed scope principle that the IPS be minimal and implementable, and the variable maturity and operational methods of existing national patient summaries, the proposal is that this first version should not attempt to require the full detail of that provenance specification.
The approach proposed for this version of the IPS is to:
- Require document-level, not section level, provenance.
- Define IPS document provenance as one of two types: human-curated or software-assembled.
- The classification is based on whether the IPS document is constructed by a human or an automated process, regardless of whether the IPS contains some content of both kinds.
- Require the IPS source system to identify the IPS document provenance type and "author".
- The "author" shall be a human, if the IPS provenance type is "human-curated", or a device or system if the IPS provenance type is "software-assembled".
- In the case of a "software-assembled" IPS that is then verified by a human, the document provenance type shall be "software-assembled" and the author shall be the device or system that constructed the IPS document, but an additional "verifier" identity shall name the human who performed this check. For the avoidance of doubt, this is not the same as legalAuthenticator. However, in cases where the verifying person intentionally wishes to sign the document, this shall be recorded as a legalAuthenticator.
- Allow optional section level author, provenance type, verifier and informant identification, for IPS source systems that can support this.
- Not attempt to implement the US Realm CDA data provenance templates.
The discussions with the EHR work group suggest that a possible future project should be an IPS functional profile, once there is greater clarity and operational experience of using the IPS.
General Implementation Guidance
- How to populate IDs in an CDA XML instance, e.g. ClinicalDocument.id, setId
- Where I can get IDs
- Relevant times for a patient summary
- Description of the different status definitions (condition, concern, observation) --> Giorgio
- (Authorship is probably a part to go to Provenance)
Cite error: <ref> tags exist for a group named "Figure", but no corresponding <references group="Figure"/> tag was found, or a closing </ref> is missing